Causes and Symptoms of Foot Pain:

Foot pain can affect any part of your foot, from your toes to your Achilles tendon at the back of your heel. Some foot pain is just an annoyance, but foot pain can also be more serious, especially if it’s the result of an injury or certain chronic conditions. Minor foot pain usually responds well to home treatment but more severe foot pain needs medical attention. If not treated, some types of foot pain can lead to long-term damage or disability.
Causes of Foot Pain
Most foot pain is due to poorly fitting shoes, injury or overuse. But structural defects and medical conditions, such as arthritis and diabetes, also can lead to foot problems. Foot pain may be caused by many different conditions or injuries. Acute or repeated injury, disease, or a combination is the most common causes of foot pain. Injury is a result of forces outside the body either directly impacting the body or forcing the body into a position where a single or combination of forces results in damage to the structures of the body. Poor biomechanical alignment may lead to foot pain. Wearing shoes that are too tight or high heels can cause pain at the balls of the feet and the bones in that area. Shoes that are tied too tightly may cause pain and bruising on the top of the foot.
- Injuries such as ligament sprains, bruises, muscle strains and fractures commonly happen suddenly (acutely).
- Sprains, strains, bruises, and fractures may be the result of a single or a combination of stresses to the foot.
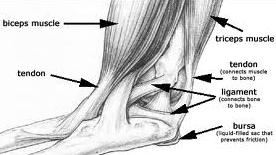
- A sprain of the foot or ankle happens when ligaments that hold the bones together are overstretched and their fibers tear.
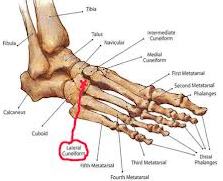
- The looseness of ligaments in the joints of the foot may lead to foot pain.
The muscle’s bursa and fascia of the foot can be strained by overstretching, overuse, overloading, bruising, or a cut (such as by stepping on a sharp object). Achilles tendonitis is a common injury to the tendon that attaches at the back of the heel.
- Injury to the bones and joints of the foot can be caused by a single blow or twist to the foot, or also by repetitive injury that can result in a stress fracture.
- A blunt-force injury such as someone stepping on your foot may result not only in a bruise (contusion) injury but also damage to the muscles and ligaments of the foot.
- Direct blows to the foot can cause bruising, breaking of the skin, or even fracturing of bones.
- Metarsalgia is the irritation of the joints of the ball of the foot. “Turf toe” is a common athletic injury in which the tendon under the joint at the base of the big toe is strained.
- Injury to the toenail can cause pooling of blood under the nail and the permanent or temporary loss of a toenail.
- Repetitive injury to the bones, muscles, and ligaments can result in extra bone growth known as spurs or exostosis.
Symptoms may accompany foot pain
Pain and point tenderness are the first indications that something is wrong in a specific area. The onset of pain, whether suddenly or over time, is an important indicator of the cause of the problem.
Bones of the foot are joined together by ligaments. A sprain happens when the ligaments that hold the bones together are overstretched and the fibers tear. Point tenderness and looseness of a joint are indications of a sprain.
Injury to the bones of the foot can be caused by a single blow or twist to the arch or also by repetitive injury that can end in a stress fracture. Fractures are indicated by a small point of pain that may be exquisitely tender on the bone. There may be a noticeable lump or gap at the site of the fracture. A turned toe or forefoot may also be a sign of a fracture.
Injury to the bones of the foot can be caused by a single blow or twist to the arch or also by repetitive injury that can end in a stress fracture. Fractures are indicated by a small point of pain that may be exquisitely tender on the bone. There may be a noticeable lump or gap at the site of the fracture. A turned toe or forefoot may also be a sign of a fracture.
Prevention of Foot Pain
- To prevent injuries and pain, the following issues should be addressed before starting an exercise routine.
- Are you in good health? A general physical exam by a physician will help to evaluate your cardiovascular function, the possibility of disease or any other general medical problems that you may have.
- Before beginning activities, diseases such as gout, diabetes, certain types of arthritis, and neuropathies should be treated.
Treatment for Foot Pain
When the pain begins to interfere with your daily living activities or if you cannot perform your chosen activities without pain, you should consider getting medical attention. Indications that you should seek medical care are:
The area looks deformed, you have loss of function, change of sensation, a large amount of swelling with pain, prolonged change of skin or toenail color, the affected area becomes warmer than the surrounding areas, becomes extremely tender to the touch, or is causing you to move differently.
At Alliance Physical Therapy we provide 24/7 access to online appointments, with most of the requests scheduled in less than 48 hours. Visit here for more information: http://www.alliancephysicaltherapyva.com